Deploying Statamic with Laravel Forge
Laravel Forge provisions and deploys PHP applications on DigitalOcean, Vultr, Akamai, AWS Hetzner and other hosting platforms. It's our favorite way to deploy Statamic.
Assuming you already have a Laravel Forge account, the first thing to do is create a server.
Creating a New Server#
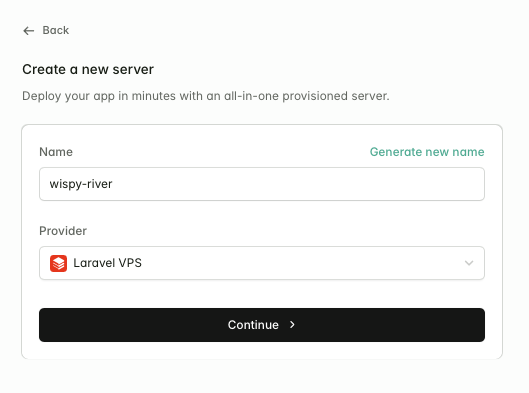
You can host your site on Laravel VPS (which is billed on top of your Forge subscription), DigitalOcean, AWS, Hetzner, or even your own fresh Ubuntu server.
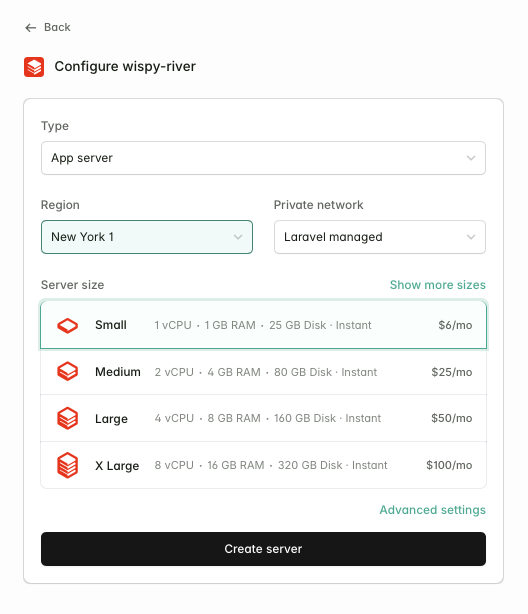
On the next screen, you'll be asked to configure your server.
For most Statamic sites, you'll want to leave the type as "App server". You should pick the region closest to your users and select a server size suitable for your project.
Once you've created your server, Forge will give you your server's sudo and database passwords. Keep these safe as you won't be able to retrieve them later.
Creating a New Site#
The next step is to create a new site. Make sure to select "Statamic" from the "New site" dropdown to take advantage of some Statamic-specific optimizations.
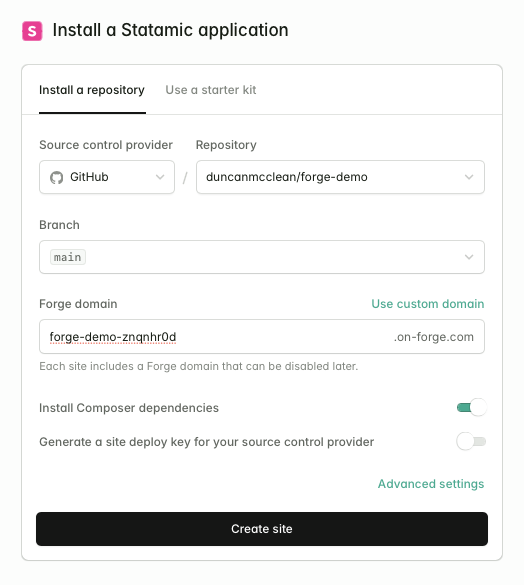
Select your Git repository, the branch you want to deploy, and configure a domain. If you don't have a domain yet, you can use a .on-forge.com subdomain.
Zero downtime deployments are disabled by default for Statamic sites, due to the additional configuration required.
Before enabling, please review our Zero Downtime Deployments guide.

Deploying#
After creating your site, Forge will take a few seconds to configure the necessary services, like Nginx and PHP-FPM, then you'll be able to trigger your first deploy.
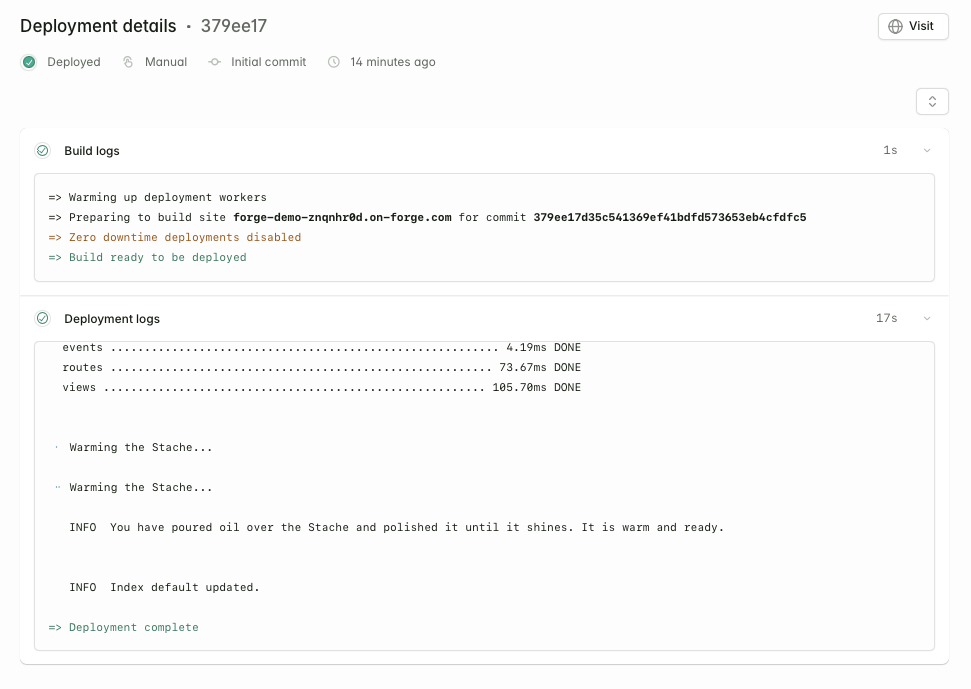
Configuring Deployments#
You can customize your deployment script under Settings -> Deployments. Your deploy script will look something like this:
cd /home/forge/forge-demo-znqnhr0d.on-forge.com
git pull origin $FORGE_SITE_BRANCH
$FORGE_COMPOSER install --no-dev --no-interaction --prefer-dist --optimize-autoloader
# Prevent concurrent php-fpm reloads...
touch /tmp/fpmlock 2>/dev/null || true
( flock -w 10 9 || exit 1
echo 'Reloading PHP FPM...'; sudo -S service $FORGE_PHP_FPM reload ) 9</tmp/fpmlock
npm ci && npm run build
if [ -f artisan ]; then
$FORGE_PHP artisan optimize
$FORGE_PHP please stache:warm
$FORGE_PHP please search:update --all
# $FORGE_PHP please static:clear
# $FORGE_PHP please static:warm --queue
fi
If you're using Static Caching, you may want to uncomment the static:clear and static:warm commands.
If you're using the Git Automation, you may want to add this snippet to the very top of your deploy script to prevent Control Panel content changes triggering full deployments.
If you're using the Eloquent Driver, you may want to comment out the $FORGE_PHP please stache:warm command and replace it with $FORGE_PHP please cache:clear.
If you want code changes to be deployed automatically when pushing to the site's branch, enable push to deploy.
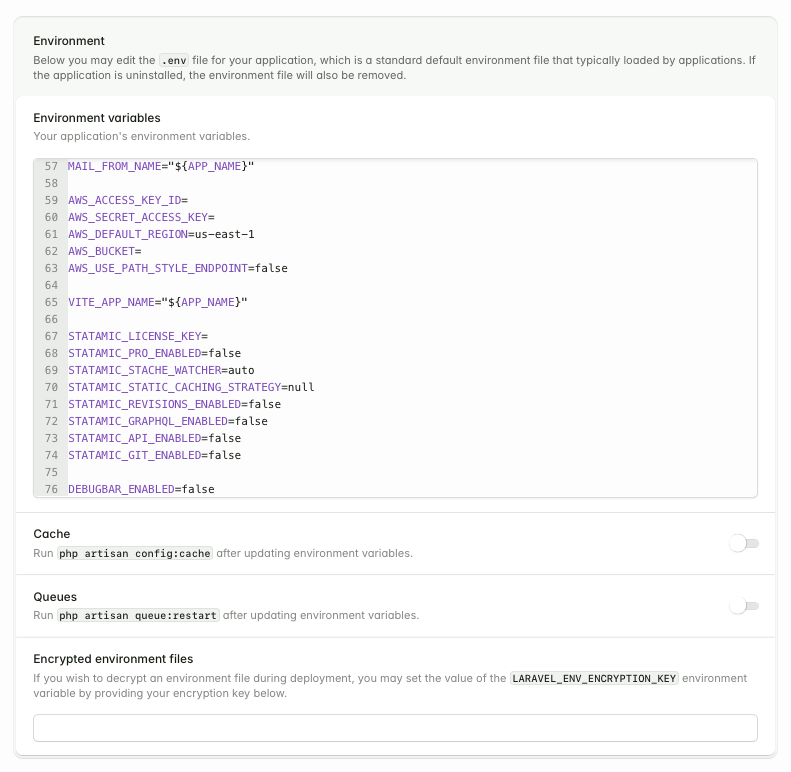
Configuring your environment#
Under Settings -> Environment, you may configure your site's environment variables. You'll find Statamic's variables near the bottom, prefixed with STATAMIC_.