Users
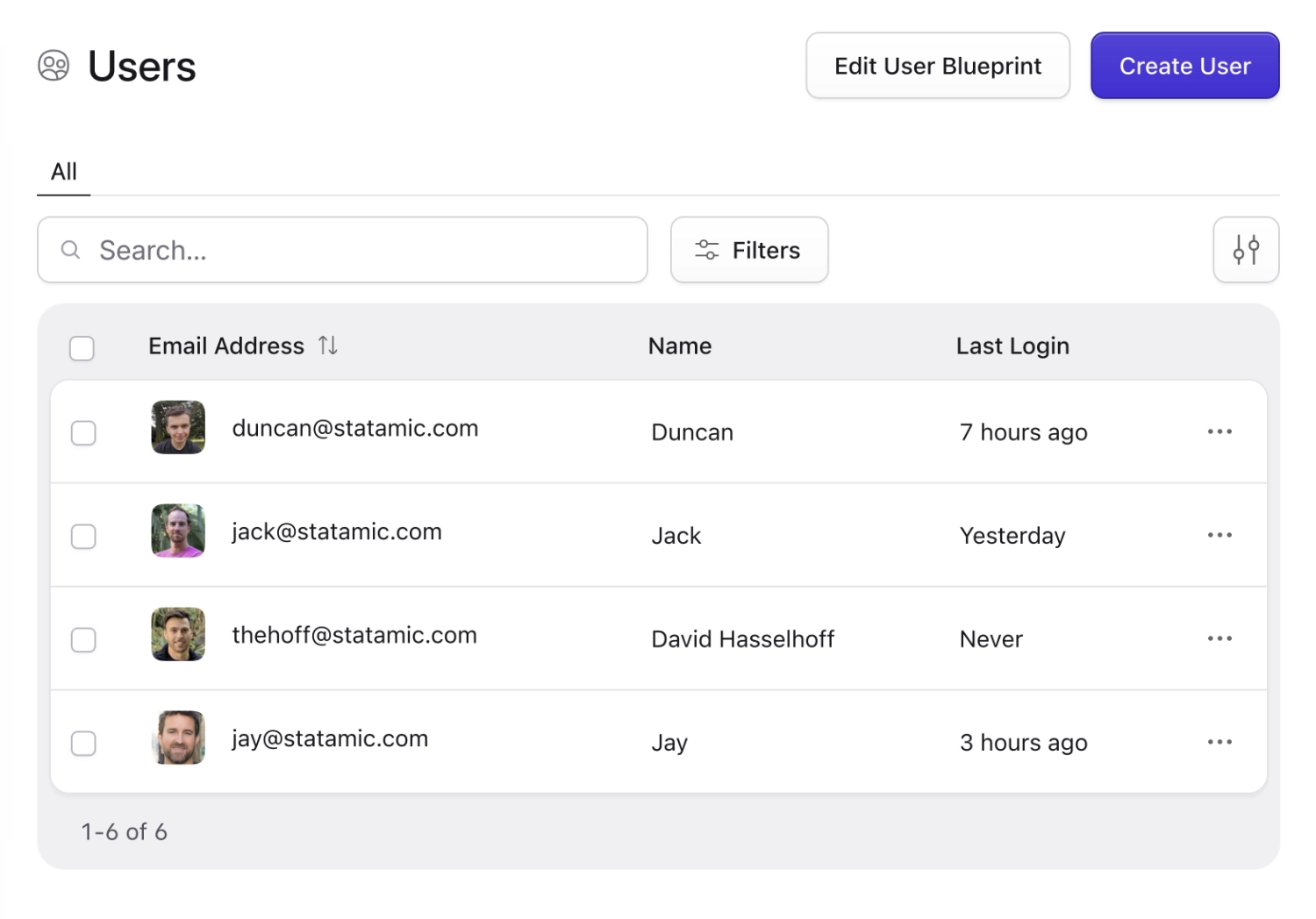
Users are the member accounts to your site or application. What a user can do with their account is up to you. They could have limited or full access to the Control Panel, a login-only area of the front-end, or even something more custom by tapping into Laravel.
Overview#
The most common and obvious reason users exist is to have the means to access the Control Panel and manage the content of your site. But there is so much more a user can do, if you so desire.
Creating users#
The easiest way to create your first user is by running php please make:user terminal command. After entering basic information, setting a password, and saying yes to super user, you can log into the control panel at example.com/cp.
You can also create users by hand in a YAML file if you'd prefer, or don't have access to the command line. And don't worry, the password field will automatically get encrypted as soon as Statamic spots it.
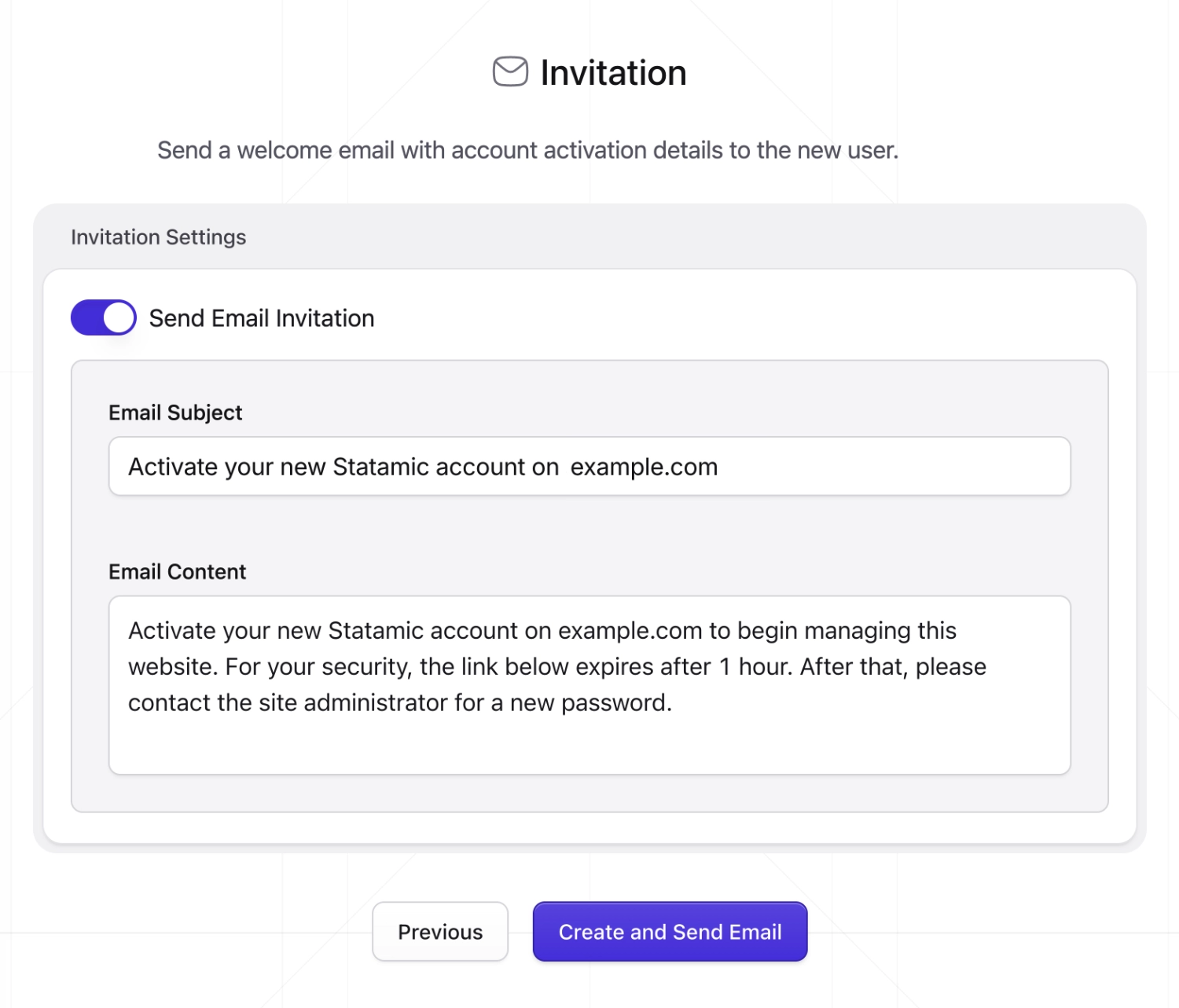
New user invitations#
When creating users in the Control Panel you can send email invitations to help guide those users into activating their accounts and signing in for the first time. You can even customize a lovely little welcome message for them.
User fields#
You're more than welcome — encouraged even — to customize what fields and information you'd like to store on your users. For example, you could store author bios and social media links to be used in articles on your front-end.
To customize these fields, edit the included user blueprint and configure it however you'd like.
Permissions#
A User by itself has no permission to access or change any aspect of Statamic. It takes explicit permissions for a user to access the control panel, create, edit, or publish content, create users, and so on.
Permissions are grouped into roles, and are very simple to manage in the Control Panel and are stored in resources/users/roles.yaml.
In turn, roles are attached directly to individual users or user groups.
Statamic's native permissions#
| Permission | Handle |
|---|---|
| Access the Control Panel | access cp |
| Configure Sites | configure sites |
| Configure Fields | configure fields |
| Configure Form Fields | configure form fields |
| Manage Preferences | manage preferences |
| Access site | access {site} site |
| Create, edit, and delete collections | configure collections |
| View entries | view {collection} entries |
| ↳ Edit entries | edit {collection} entries |
| ↳ Create entries | create {collection} entries |
| ↳ Delete entries | delete {collection} entries |
| ↳ Publish entries | publish {collection} entries |
| ↳ Reorder entries | reorder {collection} entries |
| ↳ Edit other author's entries | edit other authors {collection} entries |
| ↳ Publish other author's entries | publish other authors {collection} entries |
| ↳ Delete other author's entries | delete other authors {collection} entries |
| Create, edit, and delete navs | configure navs |
| ↳ View nav | view {nav} nav |
| ↳ Edit nav | edit {nav} nav |
| Create, edit and delete global sets | configure globals |
| Edit global variables | edit {global} globals |
| Create, edit and delete taxonomies | configure taxonomies |
| View terms | view {taxonomy} terms |
| ↳ Edit terms | edit {taxonomy} terms |
| ↳ Create terms | create {taxonomy} terms |
| ↳ Delete terms | delete {taxonomy} terms |
| Configure asset containers | configure asset containers |
| View asset container | view {container} assets |
| ↳ Upload assets | upload {container} assets |
| ↳ Edit folders | edit {container} folders |
| ↳ Edit assets | edit {container} assets |
| ↳ Move assets | move {container} assets |
| ↳ Rename assets | rename {container} assets |
| ↳ Delete assets | delete {container} assets |
| View users | view users |
| ↳ Edit users | edit users |
| ↳ Create users | create users |
| ↳ Delete users | delete users |
| ↳ Change passwords | change passwords |
| ↳ Assign user groups | assign user groups |
| ↳ Assign roles | assign roles |
| Edit user groups | edit user groups |
| Edit roles | edit roles |
| Impersonate users | impersonate users |
| View updates | view updates |
| Configure forms | configure forms |
| View form submissions | view {form} form submissions |
| ↳ Delete form submissions | delete {form} form submissions |
| Configure addons | configure addons |
| Edit addon settings | edit {addon} settings |
| Access utility | access {utility} utility |
| Resolve Duplicate IDs | resolve duplicate ids |
| View GraphQL | view graphql |
Author permissions#
Author permissions are a little bit special. They determine the control users can have over their own entries or those created by other authors.
This feature only has any effect if your entry blueprint has an author field. If you don't already have an author field, this functionality is not available.

Site permissions#
When using the multi-site feature, Statamic will check for appropriate site permissions in addition to whatever it's checking.
For example, when you try to edit a blog entry in the french site, Statamic will check if you have both the edit blog entries and access french site permissions.
Super users#
Super Admin accounts are special accounts with access and permission to everything. This includes things reserved only for super users like the ability to create more super users. It's important to prevent the robot apocalypse and this is an important firewall. We're just doing our part to save the world.
User groups#
User groups allow you to attach roles, include users, thereby assign all the corresponding permissions automatically. This approach is much simpler than assigning roles individually if you have a lot of users.
User groups are stored in resources/users/groups.yaml.
Password resets#
Let's face it. People forget their passwords. A lot, and often. Statamic supports password resets. For users with Control Panel access, the login screen (found by default at example.com/cp) already handles this for you automatically.
You can also create your own password reset pages for front-end users by using the user:forgot_password_form tag.
The user will receive an email with a temporary, single-use token allowing them to set a new password and log in again.
Password validation#
By default, passwords need to be 8 characters long. If you'd like to customize the default rules, you can use the Password rule object. (Requires at least Laravel 8.43).
These rules will be used when creating passwords throughout Statamic. In the make:user command, in the user:register_form tag, or during the password activation/reset flows. If you create the password by hand in user yaml files, the rules will be bypassed.
You can drop this into your AppServiceProvider's boot method.
use Illuminate\Validation\Rules\Password;
public function boot()
{
Password::defaults(function () {
return Password::min(16);
});
}
Consult the Laravel documentation to see all the available methods for customizing the password rule.
Storing user records#
While users are stored in files by default — like everything else in Statamic — they can also be located in a database or really anywhere else. Here are links to articles for the different scenarios you may find yourself in.
- Storing Laravel Users in Files
- Storing Users in a Database
- Custom User Storage
- Using an Independent Auth Guard
Avatars#
Each user account has an avatar field named avatar. By default it's an Assets Field that falls back to the user's initials.
This avatar is used throughout the Control Panel to represent the user when the context is important. For example, on your user dropdown menu, as an entry's "Author", or while using Real Time Collaboration.
Ordering#
By default, users are ordered alphabetically by their email. However, if you wish, you can change the field and direction used to order users in the Control Panel and when returned with the {{ users }} tag.
// config/statamic/users.php
'sort_field' => 'email',
'sort_direction' => 'asc',
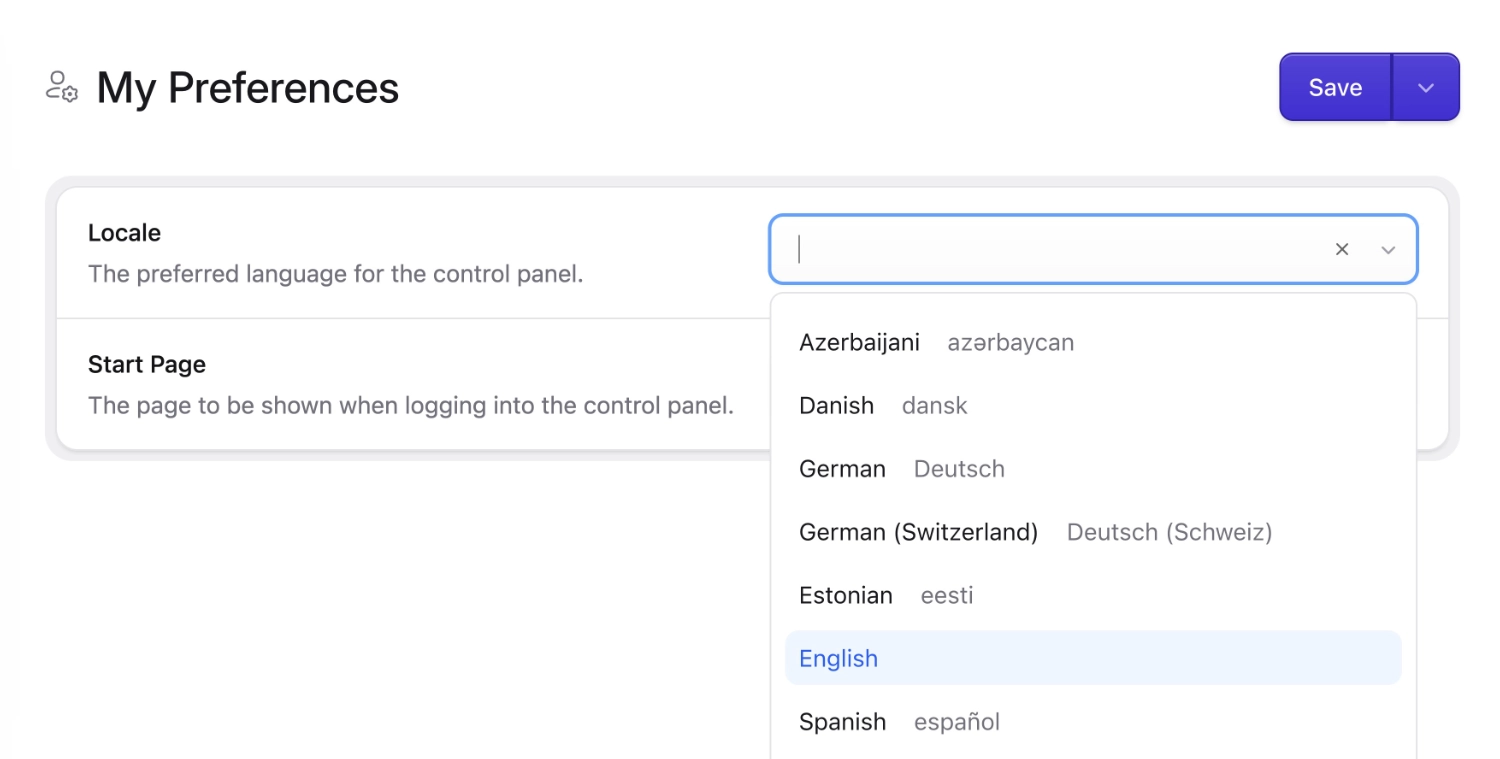
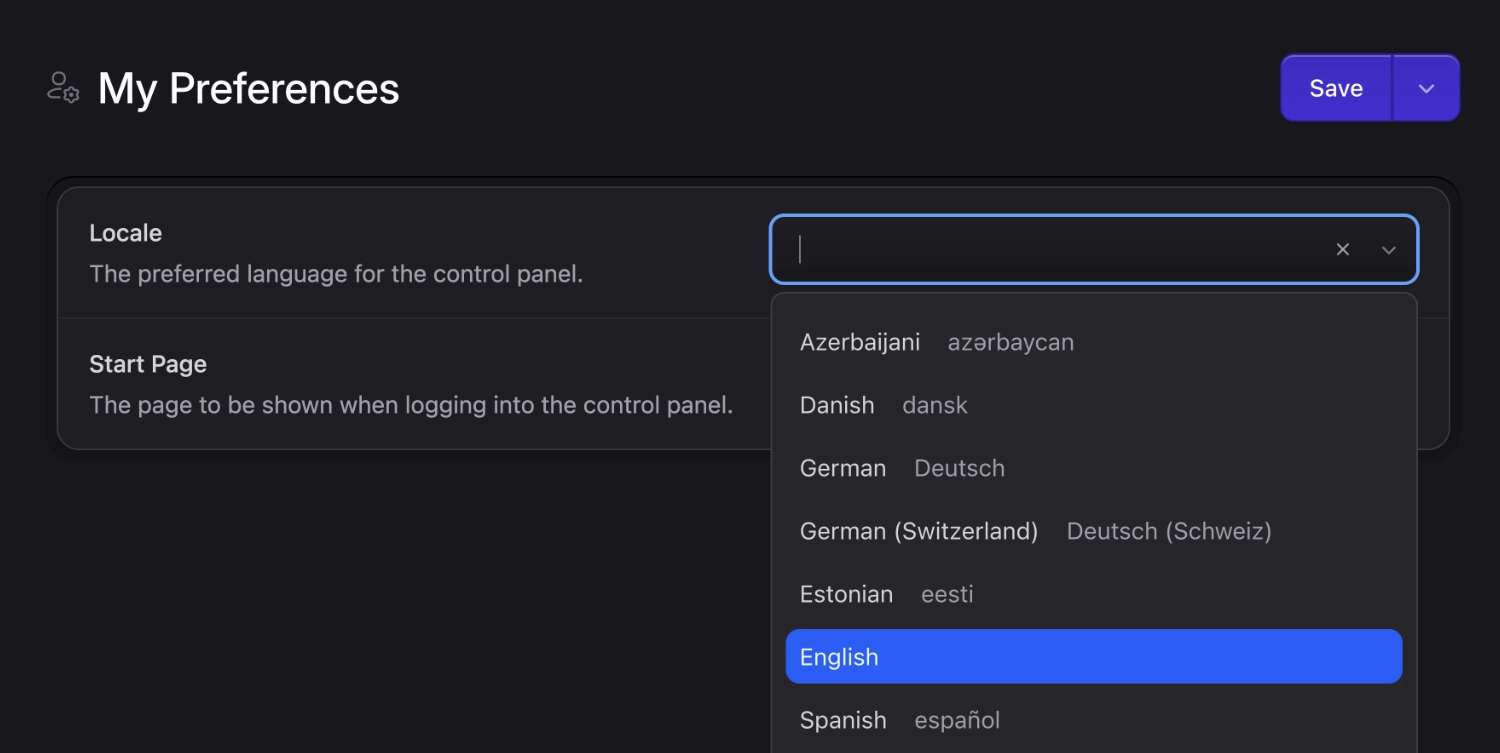
Language preference#
Each user can have their own preferred language in the Control Panel. Head to your preferences area by clicking on the ⚙️ gear/cog icon in the global header and then go to Preferences.
You can set the language for everyone by going to Default, or you can set by Role or just the current user (yourself) with Override For User.
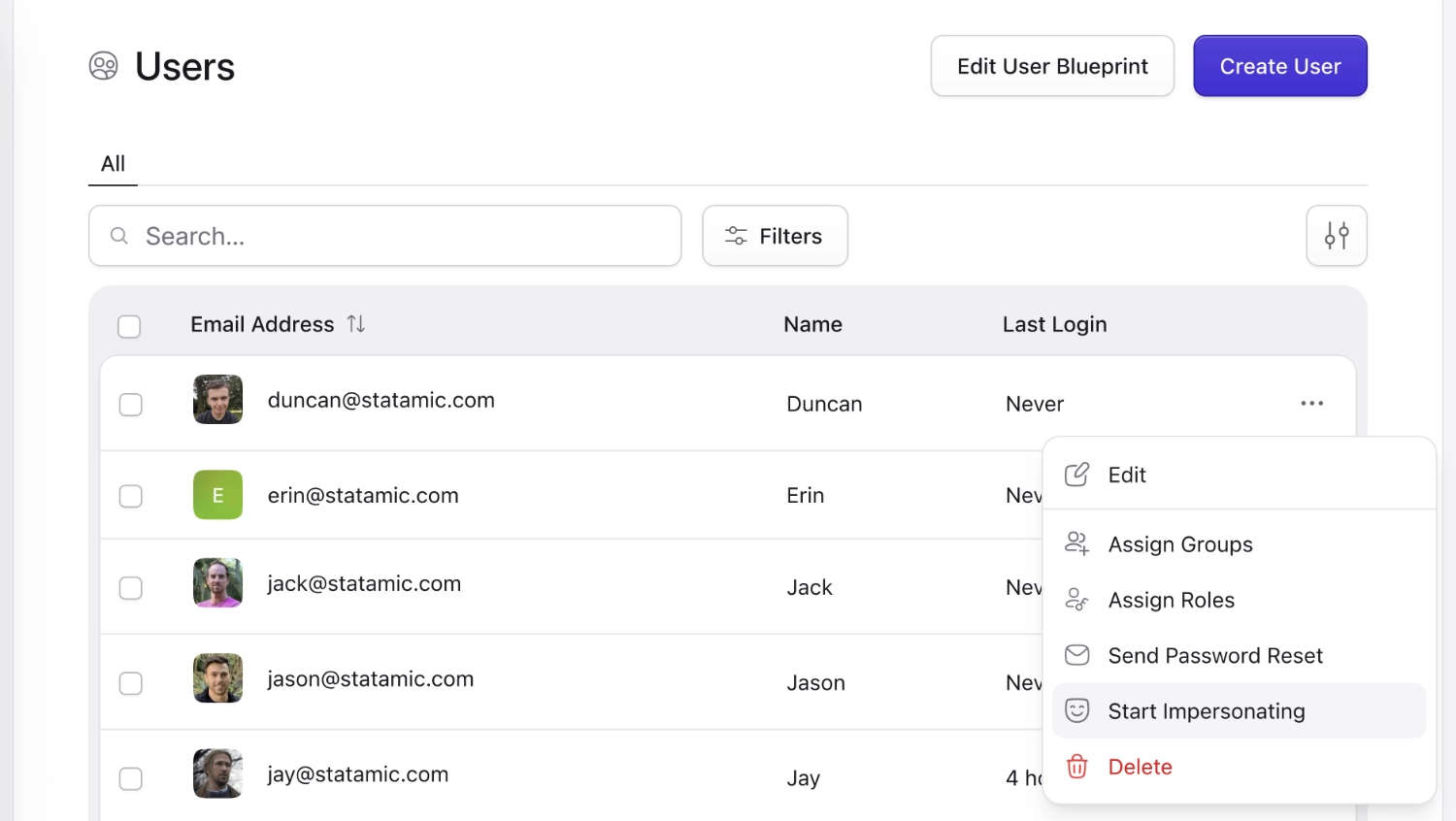
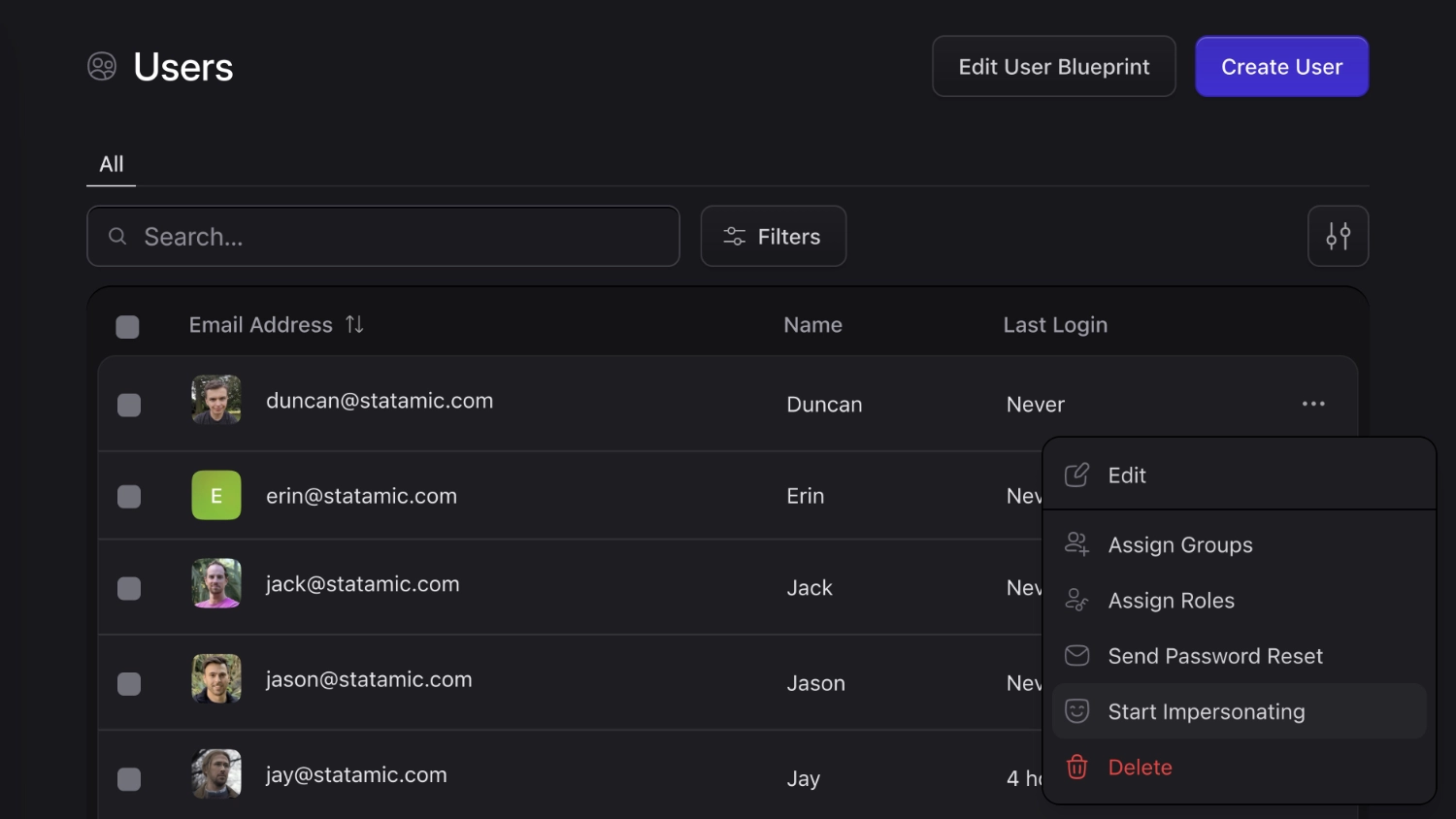
Impersonate users#
Statamic gives you the ability to impersonate users via the Control Panel. This lets you see the Control Panel and front end of your site through the eyes of the user you chose. This is pretty neat if certain content or capabilities are limited through roles and permissions and you want to test those things. It saves quite some time since there's no need to manually sign out and in again with a different user anymore.
You can configure impersonation in config/statamic/users.php, like setting the redirect destination after starting impersonation or disabling it. Additionally, there is a dedicated impersonate users permission that you can assign to roles and users to allow or disallow them using this feature.
OAuth#
In addition to conventional user authentication, Statamic also provides a simple, convenient way to authenticate with OAuth providers through Laravel Socialite. Socialite currently supports authentication with Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Google, GitHub, GitLab and Bitbucket, while dozens of additional providers are available though third-party Socialite Providers.
Learn how to configure OAuth on your site.
Two-Factor Authentication#
Statamic includes first-party support for two-factor authentication (2FA), providing an extra layer of account security.
Once enabled, users must enter a time-based one-time password (TOTP) from an authenticator app — like Google Authenticator or 1Password — alongside their password when logging in.
To enable 2FA, head to your Profile in the Control Panel. Scan the QR code with your authenticator app, enter the generated code, and you’re set. You’ll also receive a set of recovery codes — store these somewhere safe in case you lose access to your authenticator app.
2FA is optional by default, but you can enforce it for specific roles via configuration:
// config/statamic/users.php
'two_factor_enforced_roles' => [
// Enforce for everyone
'*',
// Enforce for super users
'super_users',
// Enforce for a specific role
'marketing_managers',
'user_admin',
],
Statamic uses your APP_KEY to encrypt the two-factor authentication secret and recovery codes.
You may run into issues with two-factor authentication if you have different APP_KEY values between environments and they share the same users (eg. you're tracking users in Git).

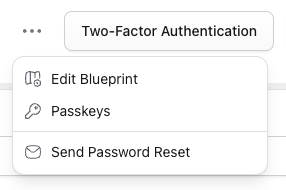
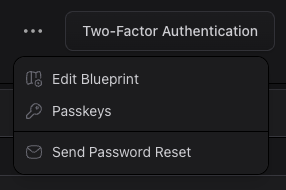
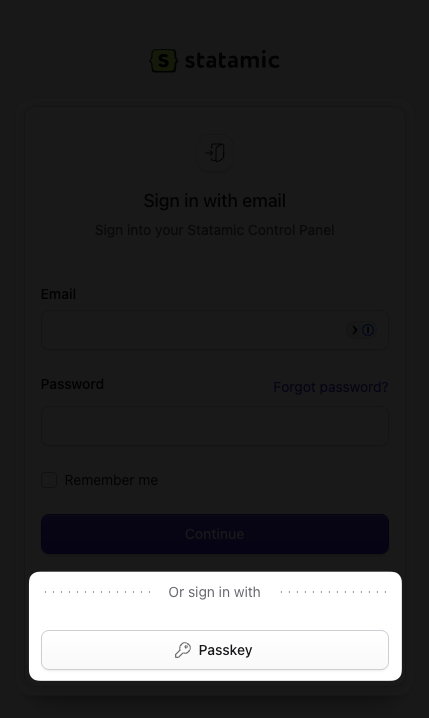
Passkeys#
Statamic supports passkeys as a secure alternative to email-and-password logins. Passkeys are a passwordless authentication method built on WebAuthn and are supported by most modern operating systems and password managers. On macOS, iOS, and iPadOS, for example, you can sign in using Touch ID or Face ID.
To add a passkey for the Control Panel, log in and visit your profile, where passkeys are managed from the Actions dropdown.
Click Create Passkey and follow the prompts to complete setup. Once a passkey has been added, you can use it to sign in without entering your email address and password.
Passkey behaviour, including whether password logins are still allowed for users with passkeys and whether “remember me” applies when logging in with a passkey, can be configured in config/statamic/webauthn.php.